What is a Thermal Imaging Survey?
Thermal imaging surveys use infrared cameras to detect and measure heat patterns in buildings and equipment. This non-invasive method helps identify issues such as heat loss, moisture accumulation, and electrical faults—providing valuable insights without the need for intrusive investigation.
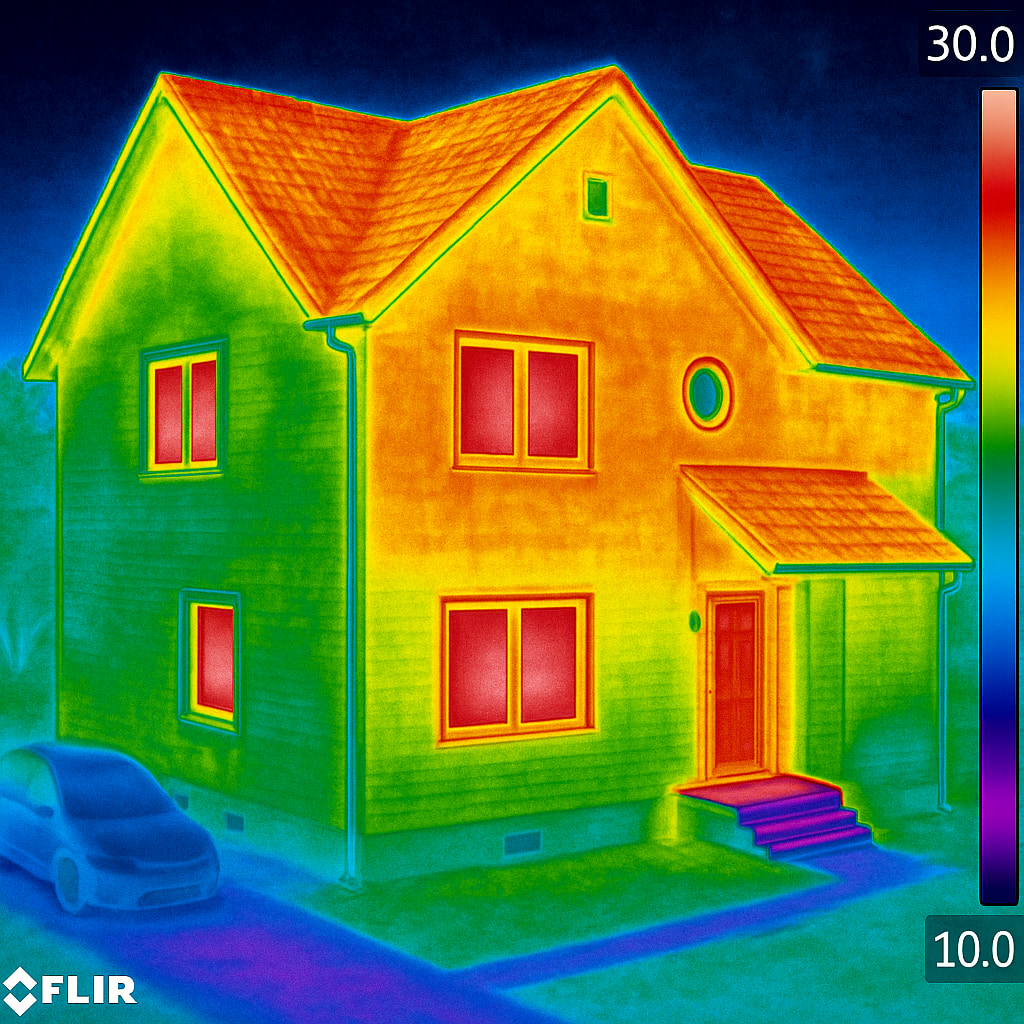
Key Aspects of Thermal Imaging Surveys:
Purpose:
To identify temperature variations, which can indicate problems such as heat loss, moisture, or electrical faults.
To provide non-invasive diagnostics without damaging the structure or equipment.
How It Works:
Thermal imaging cameras detect infrared radiation (heat) emitted by objects.
The camera converts this data into a thermographic image (a heat map) where different colors represent temperature differences.
Cold areas typically appear in blue or green, while warm areas appear in red, orange, or yellow.
Applications:
Building and Construction: Detecting heat loss through walls, roofs, and windows; locating missing or damaged insulation; identifying damp or water ingress.
Electrical Systems: Finding overheating components, faulty wiring, or overloaded circuits.
Plumbing: Identifying leaks in pipes and tracing underfloor heating systems.
Energy Audits: Assessing energy efficiency and pinpointing areas for improvement.
Mechanical Equipment: Detecting overheating parts in machinery.
Pest Detection: Spotting nests or infestations based on heat signatures.
Benefits:
Non-Invasive: No need to drill, dismantle, or disrupt structures.
Fast and Accurate: Provides real-time diagnostics with high precision.
Cost-Effective: Helps prevent expensive repairs by catching issues early.
Versatile: Suitable for a wide range of applications and industries.
Safe: Reduces the need for close contact with hazardous areas.
Tools and Techniques:
Infrared cameras are calibrated to detect heat emissions with high sensitivity.
Reports include both thermal images and corresponding photographs for context.
Advanced software analyzes thermal images to produce detailed reports.
Survey Output:
Heat loss or gain.
Moisture or water damage.
Electrical or mechanical faults.
Recommendations for repairs or improvements.
Who Needs a Thermal Imaging Survey?
Homeowners: Seeking to improve energy efficiency or investigate potential issues.
Property Buyers: To uncover hidden problems before completing a purchase.
Construction Professionals: For quality assurance and building performance checks.
Facility Managers: To support routine maintenance and ensure safety compliance.
Engineers and Electricians: When troubleshooting complex systems and equipment.
Thermal imaging surveys are invaluable for diagnosing problems, improving efficiency, and maintaining safety. By identifying issues early, they help save money and extend the lifespan of buildings and equipment.